Press Release
The Cosmic Dance of Distant Galaxies
GIRAFFE at VLT reveals the turbulent life of distant galaxies
15 March 2006
Studying several tens of distant galaxies, an international team of astronomers found that galaxies had the same amount of dark matter relative to stars 6 billion years ago as they have now. If confirmed, this suggests a much closer interplay between dark and normal matter than previously believed. The scientists also found that as many as 4 out of 10 galaxies are out of balance. These results shed a new light on how galaxies form and evolve since the Universe was only half its current age.
"This may imply that collisions and merging are important in the formation and evolution of galaxies", said François Hammer, Paris Observatory, France, and one of the leaders of the team [1].
The scientists were interested in finding out how galaxies that are far away - thus seen as they were when the Universe was younger - evolved into the ones nearby. In particular, they wanted to study the importance of dark matter in galaxies.
"Dark matter, which composes about 25% of the Universe, is a simple word to describe something we really don't understand," said Hector Flores, co-leader. "From looking at how galaxies rotate, we know that dark matter must be present, as otherwise these gigantic structures would just dissolve."
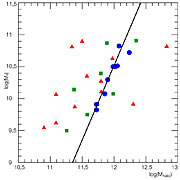
In nearby galaxies, and in our own Milky Way for that matter, astronomers have found that there exists a relation between the amount of dark matter and ordinary stars: for every kilogram of material within a star there is roughly 30 kilograms of dark matter. But does this relation between dark and ordinary matter still hold in the Universe's past?
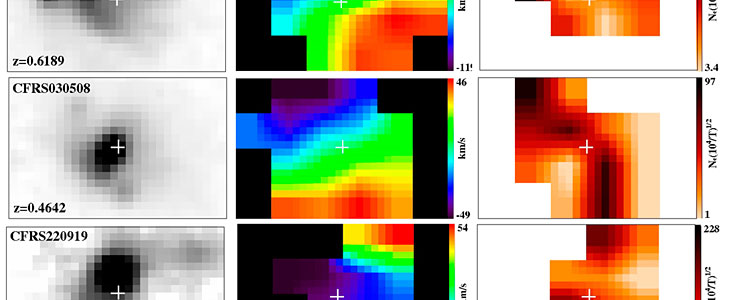
This required measuring the velocity in different parts of distant galaxies, a rather tricky experiment: previous measurements were indeed unable to probe these galaxies in sufficient detail, since they had to select a single slit, i.e. a single direction, across the galaxy.
Things changed with the availability of the multi-object GIRAFFE spectrograph [2], now installed on the 8.2-m Kueyen Unit Telescope of ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT) at the Paranal Observatory (Chile).
In one mode, known as "3-D spectroscopy" or "integral field", this instrument can obtain simultaneous spectra of smaller areas of extended objects like galaxies or nebulae. For this, 15 deployable fibre bundles, the so-called Integral Field Units (IFUs) are used to make meticulous measurements of distant galaxies. Each IFU is a microscopic, state-of-the-art two-dimensional lens array with an aperture of 3 x 2 arcsec2 on the sky. It is like an insect's eye, with twenty micro-lenses coupled with optical fibres leading the light recorded at each point in the field to the entry slit of the spectrograph.
"GIRAFFE on ESO's VLT is the only instrument in the world that is able to analyze simultaneously the light coming from 15 galaxies covering a field of view almost as large as the full moon," said Mathieu Puech, lead author of one the papers presenting the results [3]. "Every galaxy observed in this mode is split into continuous smaller areas where spectra are obtained at the same time."
The astronomers used GIRAFFE to measure the velocity fields of several tens of distant galaxies, leading to the surprising discovery that as much as 40% of distant galaxies were "out of balance" - their internal motions were very disturbed - a possible sign that they are still showing the aftermath of collisions between galaxies.
When they limited themselves to only those galaxies that have apparently reached their equilibrium, the scientists found that the relation between the dark matter and the stellar content did not appear to have evolved during the last 6 billions years.
Thanks to its exquisite spectral resolution, GIRAFFE also allows for the first time to study the distribution of gas as a function of its density in such distant galaxies. The most spectacular results reveal a possible outflow of gas and energy driven by the intense star-formation within the galaxy and a giant region of very hot gas (HII region) in a galaxy in equilibrium that produces many stars.
"Such a technique can be expanded to obtain maps of many physical and chemical characteristics of distant galaxies, enabling us to study in detail how they assembled their mass during their entire life," said François Hammer. "In many respects, GIRAFFE and its multi-integral field mode gives us a first flavour of what will be achieved with future extremely large telescopes."
Notes
[1] The team comprises: François Hammer, Hector Flores, Mathieu Puech, Chantal Balkowski (GEPI - Observatoire de Paris), Philippe Amram (LAM - Observatoire Astronomique Marseille-Provence), Göran Östlin (Stockholm Observatory), Thomas Marquart (Dept. of Astronomy and Space Physics - Uppsala, Sweden) and Matthew D. Lehnert (MPE, Germany).
[2] This complex and unique instrument allows obtaining high-quality spectra of a large variety of celestial objects, from individual stars in the Milky Way and other nearby galaxies, to very distant galaxies. It functions by means of multiple optical fibres that guide the light from the telescope's focal plane into the entry slit of the spectrograph. Here the light is dispersed into its different colours. GIRAFFE and these fibres are an integral part of the advanced Fibre Large Array Multi-Element Spectrograph (FLAMES) facility which also includes the OzPoz positioner and an optical field corrector. It is the outcome of a collaboration between ESO, Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, Observatoire de Genève-Lausanne and the Anglo Australian Observatory (AAO). More details are available in eso0203. The principle of this instrument involves the positioning in the telescope's focal plane of a large number of optical fibres. This is done in such a way that each of them guides the light from one particular celestial object towards the spectrograph that records the spectra of all these objects simultaneously. The size of the available field-of-view is no less than about 25 arcmin across, i.e. almost as large as the full moon. The individual fibres are moved and positioned "on the objects" in the field by means of the OzPoz positioner. See also eso0219.
[3] The results will be published in a series of three papers in the leading research journal, Astronomy and Astrophysics (click on the title to access the papers):
"3D spectroscopy with VLT/GIRAFFE - I: The true Tully-Fisher relationship at z~ 0.6" (Flores H., Hammer F., Puech M. et al.);
"3D spectroscopy with VLT/GIRAFFE - II: Are Luminous Compact Galaxies merger remnants?" (Puech M., Hammer F., Flores H. et al.); and
"3D spectroscopy with VLT/GIRAFFE - III: Mapping electron densities in distant galaxies" (Puech M., Flores H., Hammer F. & Lehnert M.D.).
Contacts
François Hammer
Observatoire de Paris
Paris, France
Tel: +33 (0)1 45 07 74 08
Email: francois.hammer@obspm.fr
Hector Flores
Observatoire de Paris
Paris, France
Tel: +33 (0)1 45 07 75 25
Email: hector.flores@obspm.fr
Mathieu Puech
Observatoire de Pari
Paris, France
Tel: +33 (0)1 45 07 71 43
Email: mathieu.puech@obspm.fr
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0610 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 10/06 |
| Name: | Galaxies, GIRAFFE |
| Type: | Early Universe : Galaxy |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | FLAMES |
| Science data: | 2006A&A...455..131P 2006A&A...455..119P 2006A&A...455..107F |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.