Press Release
Double Planet Meets Triple Star - High-Resolution VLT Image of Pluto Event on July 20, 2002
28 August 2002
A rare celestial phenomenon involving the distant planet Pluto has occurred twice within the past month. Seen from the Earth, this planet moved in front of two different stars on July 20 and August 21, respectively, providing observers at various observatories in South America and in the Pacific area with a long awaited and most welcome opportunity to learn more about the tenuous atmosphere of that cold planet. On the first date, a series of very sharp images of a small sky field with Pluto and the star was obtained with the NAOS-CONICA (NACO) adaptive optics (AO) camera mounted on the ESO VLT 8.2-m YEPUN telescope at the Paranal Observatory.
With a diameter of about 2300 km, Pluto is about six times smaller than the Earth. Like our own planet, it possesses a relatively large moon, Charon, measuring 1200 km across and circling Pluto at a distance of about 19,600 km once every 6.4 days. In fact, because of the similarity of the two bodies, the Pluto-Charon system is often referred to as a double planet .
At the current distance of nearly 4,500 million km from the Earth, Pluto's disk subtends a very small angle in the sky, 0.107 arcsec. It is therefore very seldom that Pluto - during its orbital motion - passes exactly in front of a comparatively bright star. Such events are known as "occultations", and it is difficult to predict exactly when and where on the Earth's surface they are visible.
Stellar occultations
When Pluto moves in front of a star, it casts a "shadow" on the Earth's surface within which an observer cannot see the star, much like the Earth's Moon hides the Sun during a total solar eclipse. During the occultation event, Pluto's "shadow" also moves across the Earth's surface. The width of this shadow is equal to Pluto's diameter, i.e. about 2300 km.
One such occultation event was observed in 1988, and two others were expected to occur in 2002, according to predictions published in 2000 by American astronomers Steve W. McDonald and James L. Elliot (Massachussetts Institute of Technology [MIT], Cambridge, USA). Further refinements provided by other observers later showed that the first event would be visible from South America on July 20, 2002, while a second one on August 21 was expected to be observable in the Pacific basin, from the western coast of North America down to Hawaii and New Zealand.
A stellar occultation provides a useful opportunity to study the planetary atmosphere, by means of accurate photometric measurements of the dimming of the stellar light, as the planet moves in front of the star. The observed variation of the light intensity and colour provides crucial information about the structure (atmospheric layers) and composition of different gases and aerosols. More information is available in the Appendix below.
The July 20 occultation
In order to profit from the rare opportunity to learn more about Pluto and its atmosphere, a large campaign involving more than twenty scientists and engineers from the Paris Observatory and associated institutions [1] was organized to observe the July 20, 2002, event involving an occultation of a star of visual magnitude 11 (i.e., about 100 times fainter than what can be perceived with then unaided eye), referred to as "P126" in McDonald and Elliot's catalogue.
In May 2002, preparatory observations showed that star to be double, with the brighter component of the system ("P126 A") being likely to be occulted by Pluto, as seen from South America. However, because of the duplicity, the predictions of exactly where the shadow of Pluto would sweep the ground were uncertain by about 0.1 arcsec in the sky, corresponding to more than 2000 km on the ground.
The NACO images
In the end, the close approach (an "appulse" in astronomical terminology) of Pluto and P126 A was indeed observed from various sites in South America, with several mobile telescopes and also including major facilities at the ESO La Silla and Paranal Observatories. In particular, unique and very sharp images were obtained with the NAOS-CONICA (NACO) adaptive optics (AO) camera mounted on the ESO VLT 8.2-m YEPUN telescope . One of the NACO images is shown in ESO Press Photos eso0224b-c . These images were made during the final adjustments of the NACO instrument and in anticipation of the upcoming science verification observations. All frames are now publicly available from the NACO data webpage on the ESO site.
The NACO image shown was obtained in infrared light (in the K-band at wavelength 2.2 µm) on July 20, 2002, some 45 min before Pluto's shadow passed north of Paranal (ESO Press Photo eso0224a). The orientation is such that North is up, and East is left. The small sky field measures about 7 x 7 arcsec 2. The pixel size is 0.027 arcsec, and the achieved image sharpness corresponds to the theoretical limit (the diffraction limit) with a telescope of this size and at this wavelength (0.07 arcsec).
The object at the centre is the star P126 A of K-magnitude 9.5 (see also ESO Press Photo eso0224c where the objects are identified), while the brighter object at the right is the companion star P126 B, 2.25 arcsec away. As P126 B is very red (of stellar type M), it appears brighter than P126 A at this infrared wavelength - the opposite is true in visible light. The intensity of the left part of the image has been multiplied by a factor of approximately 35 in order to better display Pluto and its moon Charon, located some 0.5 arcsec to the lower left (SE) of the planet. Note also the faint star "P126 C", at this moment very close to Pluto; it is probably a (physical) member of the P126 system.
A closer inspection of the original image shows that the disk of Pluto (with a diameter of 0.107 arscec and covering 16 NACO pixels) is (barely) resolved.
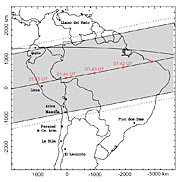
Many images were taken by NACO prior to the occultation. They will allow to retrace the precise motion of Pluto relative to P126 A, thereby improving the mapping of the motion of Pluto's shadow on the ground, cf. ESO Press Photo eso0224a . This is important in order to apply the correct geometrical circumstances for the interpretation of the photometric observations. A first evaluation of the NACO data indicates that the Paranal site "missed" the upper layers of Pluto's atmosphere by a mere 200 km or so - this is equivalent to no more than one hundredth of an arcsec as projected on the sky.
Notes
[1] The group from the Observatoire de Paris and other observatories is lead by Bruno Sicardy and also includes François Colas, Thomas Widemann, Françoise Roques, Christian Veillet, Jean-Charles Cuillandre, Wolfgang Beisker, Cyril Birnbaum, Kate Brooks, Audrey Delsanti, Pierre Drossart, Agnès Fienga, Eric Gendron, Mike Kretlow, Anne-Marie Lagrange, Jean Lecacheux, Emmanuel Lellouch, Cédric Leyrat, Alain Maury, Elisabeth Raynaud, Michel Rapaport, Stefan Renner and Mathias Schultheis . From ESO participated Nancy Ageorges, Olivier Hainaut, Chris Lidman and Jason Spyromilio .
More information
A full report on the NACO observations and other results by the present group of astronomers, also from the subsequent occultation of another star on August 21, 2002, that was extensively observed with the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) on Mauna Kea (Hawaii, USA), is available at this URL:
http://despa.obspm.fr/~sicardy/pluton/results.html
Appendix: Stellar occultations and Pluto's atmosphere
Stellar occultations are presently the only way to probe Pluto's tenuous atmosphere . When the star moves behind the planet, the stellar rays suffer minute deviations as they are refracted (i.e., bent and defocussed) by the planet's atmospheric layers. This effect, together with the large distance to the planet, manifests itself as a gradual decline of observed intensity of the stellar light, rather than an abrupt drop as this would be the case if the planet had no atmosphere.
Pluto's atmosphere was first detected on August 19, 1985, during a stellar occultation observed from Israel and then studied in more detail from Australia and from the Kuiper Airborne Observatory (KAO) during another such event on July 9, 1988. However, Pluto's atmosphere is still not well understood. It appears to be mostly composed of a dominant gas of atomic weight 28, probably molecular nitrogen (N 2). Near-IR solar reflection spectra have since shown a small presence of methane (CH 4), probably at a level of about 1% relative to nitrogen.
The 1988 occultation clearly revealed two different layers in Pluto's atmosphere, a rather smooth and isothermal outer part, and a more complex one near the planet's surface, with the possible presence of an inversion layer (in which the temperature increases with altitude) or possibly haze of photochemical origin.
The present observations aimed at discriminating between the current theoretical models of Pluto's atmosphere by means of detailed measurements of the changing intensity and colour of the stellar light, as the star is seen through progressively lower layers of the planet's atmosphere.
Another important issue is the question of whether Pluto's atmosphere has changed since 1988. In the intervening 14 years, the planet has moved away from the Sun in its elliptic orbit, whereby there has been a change in the insolation (solar flux) of about 6%. This effect might possibly have caused changes in the surface temperature and in the overall atmospheric structure of Pluto. However, any firm conclusions will have to await a complete and careful evaluation of all available observations.
Contacts
Bruno Sicardy
LESIA - Observatoire de Paris
Paris, France
Tel: +33-1-45 07 71 15
Email: bruno.sicardy@obspm.fr
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0224 |
| Legacy ID: | Photo 21a-c/02 |
| Name: | Charon, Pluto |
| Type: | Solar System : Interplanetary Body : Dwarf planet |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | NACO |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.