Press Release
A Portrait of One Hundred Thousand and One Galaxies
Rich and Inspiring Experience with NGC 300 Images from the ESO Science Data Archive
7 August 2002
A series of wide-field images centred on the nearby spiral galaxy NGC 300 , obtained with the Wide-Field Imager (WFI) on the MPG/ESO 2.2-m telescope at the La Silla Observatory, have been combined into a magnificent colour photo. These images have been used by different groups of astronomers for various kinds of scientific investigations, ranging from individual stars and nebulae in NGC 300, to distant galaxies and other objects in the background. This material provides an interesting demonstration of the multiple use of astronomical data, now facilitated by the establishment of extensively documented data archives, like the ESO Science Data Archive that now is growing rapidly and already contains over 15 Terabyte. Based on the concept of Astronomical Virtual Observatories (AVOs) , the use of archival data sets is on the rise and provides a large number of scientists with excellent opportunities for front-line investigations without having to wait for precious observing time. In addition to presenting a magnificent astronomical photo, the present account also illustrates this important new tool of the modern science of astronomy and astrophysics.
Located some 7 million light-years away, the spiral galaxy NGC 300 [1] is a beautiful representative of its class, a Milky-Way-like member of the prominent Sculptor group of galaxies in the southern constellation of that name. NGC 300 is a big object in the sky - being so close, it extends over an angle of almost 25 arcmin, only slightly less than the size of the full moon. It is also relative bright, even a small pair of binoculars will unveil this magnificent spiral galaxy as a hazy glowing patch on a dark sky background.
The comparatively small distance of NGC 300 and its face-on orientation provide astronomers with a wonderful opportunity to study in great detail its structure as well as its various stellar populations and interstellar medium. It was exactly for this purpose that some images of NGC 300 were obtained with the Wide-Field Imager (WFI) on the MPG/ESO 2.2-m telescope at the La Silla Observatory. This advanced 67-million pixel digital camera has already produced many impressive pictures, some of which are displayed in the WFI Photo Gallery [2].
With its large field of view, 34 x 34 arcmin 2, the WFI is optimally suited to show the full extent of the spiral galaxy NGC 300 and its immediate surroundings in the sky, cf. ESO Press Photo eso0221a .
NGC 300 and "Virtual Astronomy"
In addition to being a beautiful sight in its own right, the present WFI-image of NGC 300 is also a most instructive showcase of how astronomers with very different research projects nowadays can make effective use of the same observations for their programmes .
The idea to exploit one and the same data set is not new, but thanks to rapid technological developments it has recently developed into a very powerful tool for the astronomers in their continued quest to understand the Universe. This kind of work has now become very efficient with the advent of a fully searchable data archive from which observational data can then - after the expiry of a nominal one-year proprietary period for the observers - be made available to other astronomers.
The ESO Science Data Archive was established some years ago and now encompasses more than 15 Terabyte [3]. Normally, the identification of specific data sets in such a large archive would be a very difficult and time-consuming task. However, effective projects and software "tools" like ASTROVIRTEL and Querator now allow the users quickly to "filter" large amounts of data and extract those of their specific interest. Indeed, "Archival Astronomy" has already led to many important discoveries, cf. the ASTROVIRTEL list of publications.
There is no doubt that "Virtual Astronomical Observatories" will play an increasingly important role in the future, cf. eso0138. The present wide-field images ofNGC 300 provide an impressive demonstration of the enormous potential of this innovative approach. Some of the ways they were used are explained below.
Cepheids in NGC 300 and the cosmic distance scale
In 1999, Wolfgang Gieren (Universidad de Concepcion, Chile) and his colleagues started a search for Cepheid-type variable stars in NGC 300. These stars constitute a key element in the measurement of distances in the Universe. It has been known since many years that the pulsation period of a Cepheid-type star depends on its intrinsic brightness (its "luminosity"). Thus, once its period has been measured, the astronomers can calculate its luminosity. By comparing this to the star's apparent brightness in the sky, and applying the well-known diminution of light with the second power of the distance, they can obtain the distance to the star. This fundamental method has allowed some of the most reliable measurements of distances in the Universe and has been essential for all kinds of astrophysics, from the closest stars to the remotest galaxies.
Previous to Gieren's new project, only about a dozen Cepheids were known in NGC 300. However, by regularly obtaining wide-field WFI exposures of NGC 300 from July 1999 through January 2000 and carefully monitoring the apparent brightness of its brighter stars during that period, the astronomers detected more than 100 additional Cepheids . The brightness variations (in astronomical terminology: "light curves") could be determined with excellent precision from the WFI data. They showed that the pulsation periods of these Cepheids range from about 5 to 115 days. Some of these Cepheids are identified on ESO Press Photo eso0221b, in the middle of a very crowded field in NGC 300.
When fully studied, these unique observational data will yield a new and very accurate distance to NGC 300, making this galaxy a future cornerstone in the calibration of the cosmic distance scale . Moreover, they will also allow to understand in more detail how the brightness of a Cepheid-type star depends on its chemical composition, currently a major uncertainty in the application of the Cepheid method to the calibration of the extragalactic distance scale. Indeed, the effect of the abundance of different elements on the luminosity of a Cepheid can be especially well measured in NGC 300 due to the existence of large variations of these abundances in the stars located in the disk of this galaxy.
Gieren and his group, in collaboration with astronomers Fabio Bresolin and Rolf Kudritzki (Institute of Astronomy, Hawaii, USA) are currently measuring the variations of these chemical abundances in stars in the disk of NGC 300, by means of spectra of about 60 blue supergiant stars, obtained with the FORS multi-mode instruments at the ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT) on Paranal. These stars, that are among the optically brightest in NGC 300, were first identified in the WFI images of this galaxy obtained in different colours - the same that were used to produce ESO Press Photo eso0221a . The nature of those stars was later spectroscopically confirmed at the VLT.
As an important byproduct of these measurements, the luminosities of the blue supergiant stars in NGC 300 will themselves be calibrated (as a new cosmic "standard candle"), taking advantage of their stellar wind properties that can be measured from the VLT spectra. The WFI Cepheid observations in NGC 300, as well as the VLT blue supergiant star observations, form part of a large research project recently initiated by Gieren and his group that is concerned with the improvement of various stellar distance indicators in nearby galaxies (the "ARAUCARIA" project).
Clues on star formation history in NGC 300
But there is much more to discover on these WFI images of NGC 300!
The WFI images obtained in several broad and narrow band filters from the ultraviolet to the near-infrared spectral region (U, B, V, R, I and H-alpha) allow a detailed study of groups of heavy, hot stars (known as "OB associations") and a large number of huge clouds of ionized hydrogen ("HII shells") in this galaxy. Corresponding studies have been carried out by Gieren's group, resulting in the discovery of an amazing number of OB associations, including a number of giant associations.
These investigations, taken together with the observed distribution of the pulsation periods of the Cepheids, allow to better understand the history of star formation in NGC 300. For example, three distinct peaks in the number distribution of the pulsation periods of the Cepheids seem to indicate that there have been at least three different bursts of star formation within the past 100 million years. The large number of OB associations and HII shells (ESO Press Photo eso0221c) furthermore indicate the presence of a numerous, very young stellar population in NGC 300, aged only a few million years.
Dark matter and the observed shapes of distant galaxies
In early 2002, Thomas Erben and Mischa Schirmer from the "Institut für Astrophysik and extraterrestrische Forschung" (IAEF, Universität Bonn, Germany), in the course of their ASTROVIRTEL programme, identified and retrieved all available broad-band and H-alpha images of NGC 300 available in the ESO Science Data Archive. Most of these have been observed for the project by Gieren and his colleagues, described above.
However, the scientific interest of the German astronomers was very different from that of their colleagues and they were not at all concerned about the main object in the field, NGC 300. In a very different approach, they instead wanted to study those images to measure the amount of dark matter in the Universe, by means of the weak gravitational lensing effect produced by distant galaxy clusters.
Various observations, ranging from the measurement of internal motions ("rotation curves") in spiral galaxies to the presence of hot X-ray gas in clusters of galaxies and the motion of galaxies in those clusters, indicate that there is about ten times more matter in the Universe than what is observed in the form of stars, gas and galaxies ("luminous matter"). As this additional matter does not emit light at any wavelengths, it is commonly referred to as "dark" matter - its true nature is yet entirely unclear.
Insight into the distribution of dark matter in the Universe can be gained by looking at the shapes of images of very remote galaxies, billions of light-years away. Light from such distant objects travels vast distances through space before arriving here on Earth, and whenever it passes heavy clusters of galaxies, it is bent a little due to the associated gravitational field. Thus, in long-exposure, high-quality images, this "weak lensing" effect can be perceived as a coherent pattern of distortion of the images of background galaxies.
Gravitational lensing in the NGC 300 field
The WFI NGC 300 images appeared promising for gravitational lensing research because of the exceptionally long total exposure time. Although the large foreground galaxy NGC 300 would block the light of tens of thousands of galaxies in the background, a huge number of others would still be visible in the outskirts of this sky field, making a search for clusters of galaxies and associated lensing effects quite feasible. To ensure the best possible image sharpness in the combined image, and thus to obtain the most reliable measurements of the shapes of the background objects, only red (R-band) images obtained under the best seeing conditions were combined. In order to provide additional information about the colours of these faint objects, a similar approach was adopted for images in the other bands as well.
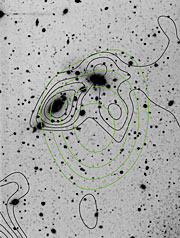
The German astronomers indeed measured a significant lensing effect for one of the galaxy clusters in the field (CL0053-37, see ESO Press Photo eso0221d); the images of background galaxies around this cluster were noticeably distorted in the direction tangential to the cluster center. Based on the measured degree of distortion, a map of the distribution of (dark) matter in this direction was constructed (ESO Press Photo eso0221e). The separation of unlensed foreground (bluer) and lensed background galaxies (redder) greatly profited from the photometric measurements done by Gieren's group in the course of their work on the Cepheids in NGC 300.
Assuming that the lensed background galaxies lie at a mean redshift of 1.0, i.e. a distance of 8 billion light-years, a mass of about 2 x 10 14 solar masses was obtained for the CL0053-37 cluster.
This lensing analysis in the NGC 300 field is part of the Garching-Bonn Deep Survey (GaBoDS), a weak gravitational lensing survey led by Peter Schneider (IAEF). GaBoDS is based on exposures made with the WFI and until now a sky area of more than 12 square degrees has been imaged during very good seeing conditions. Once complete, this investigation will allow more insight into the distribution and cosmological evolution of galaxy cluster masses, which in turn provide very useful information about the structure and history of the Universe.
One hundred thousand galaxies
In addition to allowing a detailed investigation of dark matter and lensing effects in this field, the present, very "deep" colour image of NGC 300 invites to perform a closer inspection of the background galaxy population itself.
No less than about 100,000 galaxies of all types are visible in this amazing image. Three known quasars ([ICS96] 005342.1-375947, [ICS96] 005236.1-374352, [ICS96] 005336.9-380354) with redshifts 2.25, 2.35 and 2.75, respectively, happen to lie inside this sky field, together with many interacting galaxies, some of which feature tidal tails. There are also several groups of highly reddened galaxies - probably distant clusters in formation, cf. ESO Press Photo eso0221f . Others are seen right through the outer regions of NGC 300, cf. ESO Press Photo eso0221g.
More detailed investigations of the numerous galaxies in this field are now underway. From the nearby spiral galaxy NGC 300 to objects in the young Universe, it is all there, truly an astronomical treasure trove, cf. ESO Press Photo eso0221h!
Notes
[1] "NGC" means "New General Catalogue" (of nebulae and clusters) that was published in 1888 by J.L.E. Dreyer in the "Memoirs of the Royal Astronomical Society".
[2] Other colour composite images from the Wide-Field Imager at the MPG/ESO 2.2-m telescope at the La Silla Observatory are available at the ESO Outreach website at Tarantula Nebula in the LMC.
[3] 1 Terabyte = 10 12 byte = 1000 Gigabyte = 1 million million byte.
More information
Technical information about the photos
ESO Press Photo eso0221a and all cutouts were made from 110 WFI images obtained in the B-band (total exposure time 11.0 hours, rendered as blue), 105 images in the V-band (10.4 hours, green), 42 images in the R-band (4.2 hours, red) and 21 images through a H-alpha filter (5.1 hours, red). In total, 278 images of NGC 300 have been assembled to produce this colour image, together with about as many calibration images (biases, darks and flats). 150 GB of hard disk space were needed to store all uncompressed raw data, and about 1 TB of temporary files was produced during the extensive data reduction. Parallel processing of all data sets took about two weeks on a four-processor Sun Enterprise 450 workstation. The final colour image was assembled in Adobe Photoshop. To better show all details, the overall brightness of NGC 300 was reduced as compared to the outskirts of the field.
The (red) "rings" near some of the bright stars originate from the H-alpha frames - they are caused by internal reflections in the telescope.
The images were prepared by Mischa Schirmer at the Institut für Astrophysik und Extraterrestrische Forschung der Universität Bonn (IAEF) by means of a software pipeline specialised for reduction of multiple CCD wide-field imaging camera data. The raw data were extracted from the public sector of the ESO Science Data Archive.
The extensive observations were performed at the ESO La Silla Observatory by Wolfgang Gieren, Pascal Fouque, Frederic Pont, Hermann Boehnhardt and La Silla staff, during 34 nights between July 1999 and January 2000. Some additional observations taken during the second half of 2000 were retrieved by Mischa Schirmer and Thomas Erben from the ESO archive.
CD-ROM with full-scale NGC 300 image soon available
ESO Press Photo eso0221a has been compressed by a factor 4 (2 x 2 rebinning). For ESO Press Photos eso0221b-h, the largest-size versions of the images are shown at the original scale (1 pixel = 0.238 arcsec). A full-resolution TIFF-version (approx. 8000 x 8000 pix; 200 Mb) of ESO Press Photo eso0221a will shortly be made available by ESO on a special CD-ROM, together with some other WFI images of the same size. An announcement will follow in due time.
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0221 |
| Legacy ID: | Photo 18a-h/02 |
| Name: | CL0053-37, Dark Matter, NGC 300 |
| Type: | Local Universe : Galaxy : Type : Spiral |
| Facility: | MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope |
| Instruments: | WFI |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.