Lehdistötiedote
How Old is the Milky Way ?
VLT Observations of Beryllium in Two Old Stars Clock the Beginnings
17. elokuuta 2004
Observations by an international team of astronomers [1] with the UVES spectrometer on ESO's Very Large Telescope at the Paranal Observatory (Chile) have thrown new light on the earliest epoch of the Milky Way galaxy. The first-ever measurement of the Beryllium content in two stars in a globular cluster (NGC 6397) - pushing current astronomical technology towards the limit - has made it possible to study the early phase between the formation of the first generation of stars in the Milky Way and that of this stellar cluster. This time interval was found to amount to 200 - 300 million years. The age of the stars in NGC 6397, as determined by means of stellar evolution models, is 13,400 ± 800 million years. Adding the two time intervals gives the age of the Milky Way, 13,600 ± 800 million years. The currently best estimate of the age of the Universe, as deduced, e.g., from measurements of the Cosmic Microwave Background, is 13,700 million years. The new observations thus indicate that the first generation of stars in the Milky Way galaxy formed soon after the end of the ~200 million-year long "Dark Ages" that succeeded the Big Bang.
The age of the Milky Way
How old is the Milky Way? When did the first stars in our galaxy ignite? A proper understanding of the formation and evolution of the Milky Way system is crucial for our knowledge of the Universe. Nevertheless, the related observations are among the most difficult ones, even with the most powerful telescopes available, as they involve a detailed study of old, remote and mostly faint celestial objects.
Globular clusters and the ages of stars
Modern astrophysics is capable of measuring the ages of certain stars, that is the time elapsed since they were formed by condensation in huge interstellar clouds of gas and dust. Some stars are very "young" in astronomical terms, just a few million years old like those in the nearby Orion Nebula. The Sun and its planetary system was formed about 4,560 million years ago, but many other stars formed much earlier. Some of the oldest stars in the Milky Way are found in large stellar clusters, in particular in "globular clusters" (ESO Press Photo eso0425), so called because of their spheroidal shape.
Stars belonging to a globular cluster were born together, from the same cloud and at the same time. Since stars of different masses evolve at different rates, it is possible to measure the age of globular clusters with a reasonably good accuracy. The oldest ones are found to be more than 13,000 million years old.
Still, those cluster stars were not the first stars to be formed in the Milky Way. We know this, because they contain small amounts of certain chemical elements which must have been synthesized in an earlier generation of massive stars that exploded as supernovae after a short and energetic life. The processed material was deposited in the clouds from which the next generations of stars were made, cf. ESO Press Release eso0107.
Despite intensive searches, it has until now not been possible to find less massive stars of this first generation that might still be shining today. Hence, we do not know when these first stars were formed. For the time being, we can only say that the Milky Way must be older than the oldest globular cluster stars. But how much older?
Beryllium to the rescue
What astrophysicists would like to have is therefore a method to measure the time interval between the formation of the first stars in the Milky Way (of which many quickly became supernovae) and the moment when the stars in a globular cluster of known age were formed. The sum of this time interval and the age of those stars would then be the age of the Milky Way.
New observations with the VLT at ESO's Paranal Observatory have now produced a break-through in this direction. The magic element is "Beryllium"!
Beryllium is one of the lightest elements [2] - the nucleus of the most common and stable isotope (Beryllium-9) consists of four protons and five neutrons. Only hydrogen, helium and lithium are lighter. But while those three were produced during the Big Bang, and while most of the heavier elements were produced later in the interior of stars, Beryllium-9 can only be produced by "cosmic spallation". That is, by fragmentation of fast-moving heavier nuclei - originating in the mentioned supernovae explosions and referred to as energetic "galactic cosmic rays" - when they collide with light nuclei (mostly protons and alpha particles, i.e. hydrogen and helium nuclei) in the interstellar medium.
Galactic cosmic rays and the Beryllium clock
The galactic cosmic rays travelled all over the early Milky Way, guided by the cosmic magnetic field. The resulting production of Beryllium was quite uniform within the galaxy. The amount of Beryllium increased with time and this is why it might act as a "cosmic clock".
The longer the time that passed between the formation of the first stars (or, more correctly, their quick demise in supernovae explosions) and the formation of the globular cluster stars, the higher was the Beryllium content in the interstellar medium from which they were formed. Thus, assuming that this Beryllium is preserved in the stellar atmosphere, the more Beryllium is found in such a star, the longer is the time interval between the formation of the first stars and of this star.
The Beryllium may therefore provide us with unique and crucial information about the duration of the early stages of the Milky Way.
A very difficult observation
So far, so good. The theoretical foundations for this dating method were developed during the past three decades and all what is needed is then to measure the Beryllium content in some globular cluster stars.
But this is not as simple as it sounds! The main problem is that Beryllium is destroyed at temperatures above a few million degrees. When a star evolves towards the luminous giant phase, violent motion (convection) sets in, the gas in the upper stellar atmosphere gets into contact with the hot interior gas in which all Beryllium has been destroyed and the initial Beryllium content in the stellar atmosphere is thus significantly diluted. To use the Beryllium clock, it is therefore necessary to measure the content of this element in less massive, less evolved stars in the globular cluster. And these so-called "turn-off (TO) stars" are intrinsically faint.
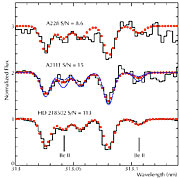
In fact, the technical problem to overcome is three-fold: First, all globular clusters are quite far away and as the stars to be measured are intrinsically faint, they appear quite faint in the sky. Even in NGC6397, the second closest globular cluster, the TO stars have a visual magnitude of ~16, or 10000 times fainter than the faintest star visible to the unaided eye. Secondly, there are only two Beryllium signatures (spectral lines) visible in the stellar spectrum and as these old stars do contain comparatively little Beryllium, those lines are very weak, especially when compared to neighbouring spectral lines from other elements. And third, the two Beryllium lines are situated in a little explored spectral region at wavelength 313 nm, i.e., in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum that is strongly affected by absorption in the terrestrial atmosphere near the cut-off at 300 nm, below which observations from the ground are no longer possible.
It is thus no wonder that such observations had never been made before, the technical difficulties were simply unsurmountable.
VLT and UVES do the job
Using the high-performance UVES spectrometer on the 8.2-m Kuyen telescope of ESO's Very Large Telescope at the Paranal Observatory (Chile) which is particularly sensitive to ultraviolet light, a team of ESO and Italian astronomers [1] succeeded in obtaining the first reliable measurements of the Beryllium content in two TO-stars (denoted "A0228" and "A2111") in the globular cluster NGC 6397 (ESO Press Photo eso0425). Located at a distance of about 7,200 light-years in the direction of a rich stellar field in the southern constellation Ara, it is one of the two nearest stellar clusters of this type; the other is Messier 4.
The observations were done during several nights in the course of 2003. Totalling more than 10 hours of exposure on each of the 16th-magnitude stars, they pushed the VLT and UVES towards the technical limit. Reflecting on the technological progress, the leader of the team, ESO-astronomer Luca Pasquini, is elated: "Just a few years ago, any observation like this would have been impossible and just remained an astronomer's dream!"
The resulting spectra (ESO Press Photo eso0425) of the faint stars show the weak signatures of Beryllium ions (Be II). Comparing the observed spectrum with a series of synthetic spectra with different Beryllium content (in astrophysics: "abundance") allowed the astronomers to find the best fit and thus to measure the very small amount of Beryllium in these stars: for each Beryllium atom there are about 2,224,000,000,000 hydrogen atoms.
Beryllium lines are also seen in another star of the same type as these stars, HD 218052, cf. ESO Press Photo eso0425. However, it is not a member of a cluster and its age is by far not as well known as that of the cluster stars. Its Beryllium content is quite similar to that of the cluster stars, indicating that this field star was born at about the same time as the cluster.
From the Big Bang until now
According to the best current spallation theories, the measured amount of Beryllium must have accumulated in the course of 200 - 300 million years. Italian astronomer Daniele Galli, another member of the team, does the calculation: "So now we know that the age of the Milky Way is this much more than the age of that globular cluster - our galaxy must therefore be 13,600 ± 800 million years old. This is the first time we have obtained an independent determination of this fundamental value!".
Within the given uncertainties, this number also fits very well with the current estimate of the age of the Universe, 13,700 million years, that is the time elapsed since the Big Bang. It thus appears that the first generation of stars in the Milky Way galaxy was formed at about the time the "Dark Ages" ended, now believed to be some 200 million years after the Big Bang.
It would seem that the system in which we live may indeed be one of the "founding" members of the galaxy population in the Universe.
Lisähuomiot
[1] The team is composed of Luca Pasquini (ESO), Piercarlo Bonifacio (INAF-Osservatorio di Trieste, Italy), Sofia Randich and Daniele Galli (INAF-Osservatorio di Arcetri, Firenze, Italy), and Raffaele G. Gratton (INAF-Osservatorio di Padova, Italy).
[2] Interestingly, the secondary mirrors of the four VLT Unit Telescopes are made of Beryllium in order to make them as light as possible while retaining the necessary stiffness. Each of the four mirrors measures 1.1 metres across and weighs about 50 kilograms.
Lisätietoa
The research presented in this press release is discussed in a paper entitled "Be in turn-off stars of NGC 6397: early Galaxy spallation, cosmochronology and cluster formation" by L. Pasquini and co-authors that will be published in the European research journal "Astronomy & Astrophysics" (astro-ph/0407524).
Yhteystiedot
Luca Pasquini
ESO
Garching, Germany
Puh.: +49-89-3200-6792
Sähköposti: lpasquin@eso.org
Daniele Galli
INAF-Osservatorio di Arcetri
Arcetri, Italy
Puh.: +39-055-2752249
Sähköposti: galli@arcetri.astro.it
Tiedotteesta
| Tiedote nr.: | eso0425 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 20/04 |
| Nimi: | NGC 6397 |
| Tyyppi: | Milky Way : Star : Grouping : Cluster : Globular |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | UVES |
| Science data: | 2007A&A...464..601P |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.