Pressemeddelelse
How Old is the Universe?
First Reading of a Basic Cosmic Chronometer with UVES and the VLT
7. februar 2001
Most astronomers would agree that the age of the Universe - the time elapsed since the "Big Bang" - is one of the "holy grails of cosmology". Despite great efforts during recent years, the various estimates of this basic number have resulted in rather diverse values. When derived from current cosmological models, it depends on a number of theoretical assumptions that are not very well constrained by the incomplete available observational data. At present, a value in the range of 10-16 billion years [1] is considered most likely. But now, an international team of astronomers [2] has used the powerful ESO Very Large Telescope (VLT) and its very efficient spectrograph UVES to perform a unique measurement that paves the way for a new and more accurate determination of the age of the Universe. They measured for the first time the amount of the radioactive isotope Uranium-238 in a star that was born when the Milky Way, the galaxy in which we live, was still forming. It is the first measurement ever of uranium outside the Solar System.
This method works in a way similar to the well-known Carbon-14 dating in archaeology, but over much longer times. Ever since the star was born, the Uranium "clock" has ticked away over the eons, unaffected by the turbulent history of the Milky Way. It now reads 12.5 billion years . Since the star obviously cannot be older than the Universe, it means that the Universe must be older than that .
Although the stated uncertainty is still about 25% or about ±3 billion years, this is only to a minor extent due to the astronomical observation. The main problem is the current absence of accurate knowledge of some of the basic atomic and nuclear properties of the elements involved. However, further laboratory work will greatly improve this situation and a more accurate value for the age of the star and implicitly, for the Universe, should therefore be forthcoming before long.
This important result is reported in the international research journal Nature in the issue of February 8, 2001.
Heavy elements in stars
While hydrogen, helium and lithium were produced during the Big Bang, all heavier elements result from nuclear reactions in the interiors of stars. When stars die, heavy-element enriched matter is dispersed into surrounding space and will later be incorporated in the next generations of stars. In fact, the gold in the ring on your finger was produced in an exploding star and deposited in the interstellar cloud from which the Sun and its planets were later formed.
Thus, the older a star is, the lower is generally its content of heavy elements like iron and other metals. Measurements have shown that old stars that are members of large agglomerations known as globular clusters are normally quite "metal-poor"- their metal-content ranges down to about 1/200 of that of the Sun, in which these metals constitute only 2% of the total mass, the rest being still in the form of hydrogen and helium.
Very old stars in the Milky Way galaxy
After decades of mostly fruitless efforts, a large spectral survey by American astronomer Timothy C. Beers and his collaborators has recently uncovered hundreds of stars with much lower metal content than even the globular clusters, in some cases only 1/10,000 of the solar value. It is evident that these extremely metal-poor stars must have formed during the very infancy of the Milky Way, an important, but still poorly understood phase in the life of our galaxy.
These particular stars exhibit a great variety of element abundances that may ultimately throw more light on the processes at work during this early period. As a step in this direction, an international team of astronomers [2] decided to study these stars in much more detail. They were awarded observing time for a Large Programme in 2000-2001 with the powerful combination of the ESO VLT and its very efficient high-dispersion spectrograph UVES. The first observations have been carried out and, not unexpectedly, have already proven to be a true gold mine of new information.
Cosmochronology with radioactive isotopes
It is possible to make a fundamental determination of the age of a star that is quite independent of stellar evolution models, provided it contains a suitable long-lived radioactive isotope [3]. The use of a "radioactive chronometer" depends on the measurement of the abundance of the radioactive isotope, as compared to a stable one.
This technique is analogous to the Carbon-14 dating method that has been so successful in archaeology over time spans of up to a few tens of thousands of years. In astronomy, however, this technique must obviously be applied to vastly longer time scales.
For the method to work well, the right choice of radioactive isotope is very critical. Contrary to stable elements that formed at the same time, the abundance of a radioactive (unstable) isotope decreases all the time. The faster the decay, the less there will be left of the radioactive isotope after a certain time, the greater will be the abundance difference when compared to a stable isotope, and the more accurate is the resulting age.
Yet, for the clock to remain useful, the radioactive element must not decay too fast - there must still be enough left of it to allow an accurate measurement, even after several billion years.
Thorium and Uranium clocks
This leaves only two possible isotopes for astronomical measurements, thorium (232 Th or Thorium-232, with a half-life of 14.05 billion years [4]) and uranium (238 U or Uranium-238, half-life 4.47 billion years).
Several age determinations have been made by means of the Thorium-232 isotope. Its strongest spectral line is measurable with current telescopes in a handful of comparatively bright stars, including the Sun. However, the decay is really too slow to provide sufficiently accurate time measurements. It takes around 47 billion years for this isotope to decay by a factor of 10, and with a typical measuring uncertainty of 25%, the resulting age uncertainty is about 4-5 billion years, or approx. one third of the age of the Universe. This slow-moving clock runs forever, but is hard to read accurately!
The faster decay of Uranium-238 would make it a much more precise cosmic clock. However, because uranium is the rarest of all normal elements, its spectral lines in stars are always very weak; if visible at all, they normally drown entirely in a vast ocean of stronger spectral lines from more abundant elements.
Nevertheless, this is exactly where the low abundance of heavier elements in very old stars comes to the rescue. In the stars that were studied by the present team at the VLT, with typically 1000 times less of the common elements than in the Sun, the predominance of the maze of atomic and molecular lines in the spectrum is greatly reduced. The lines of rare elements like uranium therefore stand a real chance of being measurable. This is particularly so, if for some reason uranium atoms were preferentially retained in the debris of those early supernova explosions that also created the iron-group elements we see in the stars today.
The uranium line in CS 31082-001
The excitement of the astronomers was great when they inspected the first spectrum of the 12th-magnitude programme star CS 31082-001! It showed what is probably the richest spectrum of rare, heavy elements ever seen. In particular, the faint lines of these elements were unusually free of interference from the lines of the iron-group elements which are indeed only 1/800 as abundant in this star as in the Sun, and by molecular lines (of CH and CN), often quite numerous even in such low-metallicity stars.
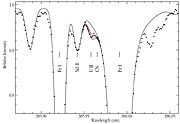
While only one or at most two thorium lines have ever been measured in any other stars, no less than 14 thorium lines are seen in the spectrum of CS 31082-001. Indeed, there is such a wealth of lines of other rare and precious metals that this spectrum is a real astronomers' treasure box. And best of all, the long sought-after line of singly ionized uranium is clearly detected at its rest wavelength of 389.59 nm in the near-ultraviolet region of the spectrum!
Not surprisingly, the uranium line is still quite weak. After all, uranium is the rarest of elements to begin with and it has further decayed by a factor of eight since this star was born. Moreover, even in this low metal-abundance star, the near-UV spectrum remains rather rich in other lines.
The accurate measurement of this faint spectral line therefore places extreme demands on the acuity (resolving power) and efficiency of the spectrograph and the light-gathering power of the telescope. The VLT and UVES have been built as the world-leading combination of these observational assets, and the spectra obtained of this comparatively faint star (magnitude 12, i.e. 500 times fainter than what can be seen with the unaided eye) are absolutely superb - indeed of a quality which until recently was reserved for naked-eye stars only. Despite its faintness, the uranium line can therefore be measured with very good accuracy.
The age of CS 31082-001
A detailed analysis, using model atmospheres and synthetic spectrum calculations, shows that all the heaviest stable elements follow closely the abundance pattern seen in the Sun, but at a level of about 12% of the corresponding solar abundances [5].
The measurements also show that the thorium and uranium abundances are somewhat lower than this - of the order of 9% and 6% of the solar values, respectively. Since these two elements were formed by the same atomic processes as their stable neighbours in the periodic table, this means that radioactive decay has progressed further in CS 31082-001 than in the Sun.
Different models of the element production in supernova explosions predict somewhat different production ratios between the stable and radioactive isotopes, leading to age estimates for this star in the range 11-16 billion years. The most likely age of CS 31082-001 is 12.5 billion years .
The Universe is older than the star, hence it must be older than 12.5 billion years.
Improved age determination soon possible
Given the faster decay rate of Uranium-238, the measuring uncertainty for the stellar uranium line corresponds to an age uncertainty of only ±1.5 Gyr. This can be further reduced with even better spectra of CS 31082-001 and/or with the discovery and observation of other similar stars.
However, for the immediate future, the accuracy of this age determination does not really depend on the VLT spectrum. For the time being, the real problems are the present uncertainties in the available laboratory data for uranium by means of which the measured line strengths are converted into element abundances. In addition, the nuclear-physics calculations of the initial isotope production ratios introduce errors that are larger than those of the spectral observation.
Thus, improved measurements of those physical data are necessary in order to read more accurately the cosmic clock in CS 31082-001 from the existing observational data. The relevant laboratory measurements are now underway at the CEA, Saclay, France, and the University of Lund, Sweden.
In the meantime, the team is trying to find other stars like CS 31082-001. There may not be many, but if the uranium line can be seen and measured in more spectra, it will also become possible to judge whether those very old stars, as surmised, are all of about the same age, i.e. that of our Milky Way galaxy.
Noter
[1] 1 billion = 1,000 million.
[2] The team members are: Roger Cayrel (P.I.), Francois Spite and Monique Spite (all Observatoire de Paris, France), Vanessa Hill and Francesca Primas (ESO), Johannes Andersen and Birgitta Nordström (Copenhagen and Lund Observatories, Denmark and Sweden), Timothy C. Beers (Michigan State Univ., USA), Piercarlo Bonifacio and Paolo Molaro (Trieste, Italy), Bertrand Plez (Montpellier, France), and Beatriz Barbuy (Univ. of Sao Paulo, Brazil).
[3] Isotopes of a natural element contain different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei, in addition to a certain number of protons that characterize that particular element. Some isotopes are "radioactive", i.e. with time they are transformed into other elements or isotopes. Other isotopes are stable over exceedingly long periods of time. Uranium-238 contains 92 protons and 146 neutrons.
[4] The "half-life" of an isotope indicates the time after which half the atoms have decayed. After another time interval of this length has passed, only 25% of the original isotope is left, etc.
[5] As the iron abundance in CS 31082-001 is only 0.12% (1/800) of that in the Sun, this means that, relative to iron and similar, lighter elements, the heaviest elements in that star are approximately 100 times "overabundant". Their spectral lines, again in relative terms, are correspondingly stronger - this is of crucial importance for the present, difficult measurements.
Mere information
The research described in this Press Release is reported in a research article ("Measurement of stellar age from uranium decay"), that appears in the international research journal Nature on Thursday, February 8, 2001.
Technical information about the photos
ESO Press Photo eso0106 is reproduced from the STScI Digitized Sky Survey (© 1993, 1994, AURA, Inc. - original plate material by Royal Observatory Edinburgh and the Anglo-Australian Observatory - All Rights Reserved) and based on blue-sensitive photographic data obtained using the UK Schmidt Telescope at Siding Spring (Australia). The comparatively empty sky field is located at high southern (-76°) galactic latitude and measures 7 x 7 arcmin 2 and. ESO Press Photo eso0106 is reproduced from a spectrum of CS 31082-001, obtained in October 2000 with the UVES high-dispersion spectrograph at the VLT 8.2-m KUEYEN telescope at Paranal. The exposure lasted 4 hours, at a spectral resolution of approx. 75,000 and with a S/N-ratio of about 300. The lines are identified and three synthetic spectra, with different U-abundances, are drawn to illustrate the fit.
Kontakter
Roger Cayrel
Observatoire de Paris-Meudon
Paris, France
Tel: +33 - 1 - 4051 - 2251
E-mail: roger.cayrel@obspm.fr
Monique Spite
Observatoire de Paris-Meudon
Paris, France
Tel: +33 - 1 - 4507 - 7840
E-mail: monique.spite@obspm.fr
Johannes Andersen
Copenhagen University Observatory
Copenhagen, Denmark
Tel: +45 - 353 - 25934
E-mail: ja@astro.ku.dk
Vanessa Hill
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49 - 89 - 3200 - 6465
E-mail: vhill@eso.org
Om pressemeddelelsen
| Pressemeddelelse nr.: | eso0106 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 02/01 |
| Navn: | CS 31082-001, Spectrum |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | UVES |
| Science data: | 2001Natur.409..691C |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.